
- Send to a friend
-
- Remove this product from my favorite's list.
- Add this product to my list of favorites.
No specials at this time
No products added yet

Covering 400% the area of Genesis, FarmBot Genesis XL can grow enough veggies for a family of four, provides ample room for student agronomy competitions, and can take research experiments to new scale. Suitable for fixed installations at home, farm to fork restaurants, universities, and commercial facilities.
Nominal machine dimensions
Note: Serviceable area will be slightly less, and the max supported plant height is approximately 0.5m
All FarmBots must be mounted to a raised bed or similar infrastructure. Neither materials for the bed nor soil are included with the kits because every installation will be different, and shipping lumber and soil would be prohibitively expensive.
FarmBot must be plugged into a 110 or 220V outlet. The 30cm (1ft) power cord comes with a standard US 3-prong plug. You must connect this to your own extension cord if needed. Customers outside the US: you must provide a plug adapter if needed.
FarmBot's water system has a 3/4″ female Garden Hose Thread (GHT) connection, meaning you can take a standard US garden hose and screw it into your FarmBot. You will need to provide a hose of the appropriate length.
FarmBot can only be controlled using the web app, so an internet connection is required. The Raspberry Pi has built-in WiFi, though you may need to reposition your WiFi router or install a repeater to ensure a reliable connection.
You control and configure FarmBot using the free FarmBot web application at my.farm.bot. We expect to indefinitely offer free service adequate for home growing needs, though we may charge for commercial or industrial FarmBot usage, for FarmBots larger than 3m x 6m in area, for FarmBots growing large numbers of plants concurrently, for multi-bot/multi-user management, for advanced features, and/or for other increased account limits. You can always host the software on your own server if you do not want to use our service.
Documentation for fixed and mobile raised beds and other supporting infrastructure options
FarmBot’s tracks need to be attached to supporting infrastructure such as a typical raised garden bed. Where you decide to install your FarmBot will determine how you setup your tracks and therefore what type of supporting infrastructure you need.



In the next sections we offer reference designs for building four types of supporting infrastructure: a fixed raised bed, a mobile raised bed, wood posts, and pier block supports. However, not every type of infrastructure is suitable for all of our kits. Refer to the table below to see our recommendations.
| Genesis | Genesis XL | |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Raised Bed | ||
| Mobile Raised Bed | ||
| Wood Posts | ||
| Pier Block Supports |
We recommend building your supporting infrastructure as large as possible to get the most value out of your FarmBot. See the economies of scale section for more information on maximizing FarmBot value.
If you are going to modify on of our reference designs, or build supporting infrastructure of your own design, use the dimension guidelines below to ensure compatibility with your FarmBot.
| FarmBot | Outer Infrastructure Width | Outer Infrastructure Length |
|---|---|---|
| Genesis | 1.36m (53.5”) max | 3m (118”) recommended |
| Genesis XL | 2.86m (112.5”) max | 6m (236”) recommended |
While you can adjust a FarmBot to accommodate smaller width infrastructure, you cannot adjust it for infrastructure larger than the maximum width listed.
While FarmBot Genesis and Genesis XL kits only include enough track extrusions and other hardware to allow for gantry travel up to 3m and 6m respectively, creating infrastructure with a longer length will not prevent the system from being installed.
Step-by-step instructions for building a fixed raised bed for FarmBot Genesis or Genesis XL
Building a fixed raised bed is the recommended method for installing FarmBot Genesis or Genesis XL outdoors. In these instructions we show you how to build a simple but sturdy bed that will fit into most yards, look great, and last a lifetime.
Documentation and assembly instructions for the FarmBot Genesis tracks
FarmBot’s tracks allow the gantry to move precisely along the x-axis. They are designed to mount directly to the top of a raised bed or similar supporting infrastructure. Each track is composed of 1.5m long aluminum extrusions positioned end-to-end to form a total track length of 3m for Genesis models and 6m for Genesis XL.
Documentation and assembly instructions for the FarmBot Genesis gantry
Documentation and assembly instructions for the FarmBot Genesis cross-slide and Z-axis
Documentation and assembly instructions for the FarmBot Genesis toolbays
Documentation for the FarmBot Genesis UTM, tools, seed containers, and camera
The Universal Tool Mount, or UTM, allows FarmBot Genesis to automatically switch tools in order to perform different operations. It features:
Documentation for FarmBot Genesis electronics
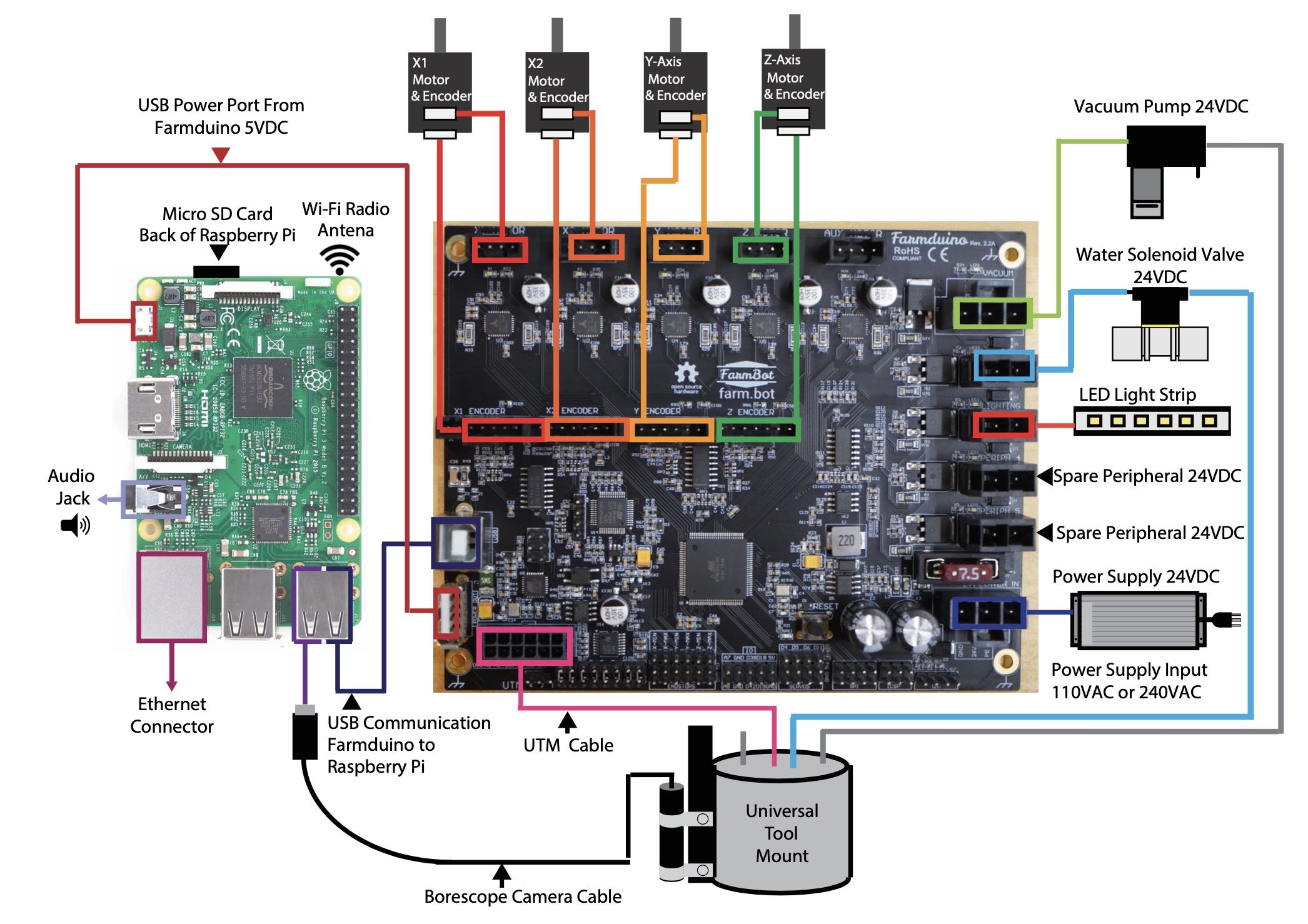
The Farmduino and Raspberry Pi are the central components of the FarmBot from an electronic systems perspective. The diagram below shows how the other electronic components connect to these boards, as well as how the two are connected to each other.
The Farmduino microcontroller uses Arduino architecture and it communicates with the Raspberry Pi using a G-code like language. The Farmduino controls the stepper drivers and motors, as well as the UTM and peripherals. The Farmduino provides power and control to all the electronic components of the FarmBot. The board has a layout and connectors that are optimized for FarmBot’s various peripherals and motor requirements.
Final steps to take now that your FarmBot is fully assembled and powered up.
You’re now ready to move onto the software portion of setting up your FarmBot. Refer to the getting started guide on our software documentation hub for instructions on how to:
Openly licensed and free to use educational resources for teaching FarmBot technology and related subjects
Welcome, and thank you for taking interest in using FarmBot as a tool to inspire the next generation of farmers! The Open Educational Resources available on this site aim to help instructors in implementing FarmBot curriculum in K-12 schools, extracurricular clubs, continuing education programs, and more across a variety of STEM subjects.
Teaching with FarmBot in schools can be a rewarding and unique experience for teachers and students alike. At its heart, our curriculum lies at the intersection of the DIY maker movement, robotics, and small-scale polycrop food production. The lesson plans and activities are hands-on and multidisciplinary, meet many common core objectives, and effectively bridge the gap between theory and the real world. In addition to being fun and engaging, students are rewarded with the real vegetables, flowers, mushrooms, and more that they learn to grow with their FarmBot.
FarmBot open educational resources are organized into four domains, with each one covering a wide range of topics, as well as the inter-relations between each topic and domain.
![]() Hardware – Mechanics, design, and material properties; using tools; reading and following technical documentation and assembly instructions; and electronics and wiring.
Hardware – Mechanics, design, and material properties; using tools; reading and following technical documentation and assembly instructions; and electronics and wiring.
![]() Software – Software basics; modularization; databases and data; APIs; and using the web app to control and configure FarmBot with the sequence builder, regimen builder, and farm designer.
Software – Software basics; modularization; databases and data; APIs; and using the web app to control and configure FarmBot with the sequence builder, regimen builder, and farm designer.
![]() Farming – Plants and their nutritional and medicinal properties; soils; the environment; and agricultural techniques, history, and impacts.
Farming – Plants and their nutritional and medicinal properties; soils; the environment; and agricultural techniques, history, and impacts.
![]() Sustainability – Climate change; the water cycle; the carbon cycle; impacts of agriculture; carbon footprint of FarmBot; lifecycle analysis of FarmBot; powering FarmBot with solar; using collected rainwater with FarmBot; food miles travelled; carbon intensity of various foods.
Sustainability – Climate change; the water cycle; the carbon cycle; impacts of agriculture; carbon footprint of FarmBot; lifecycle analysis of FarmBot; powering FarmBot with solar; using collected rainwater with FarmBot; food miles travelled; carbon intensity of various foods.
To get started, browse through the topics listed in the left-hand menu.
The resources available on this site have been developed to help instructors meet specific Common Core (CC) and Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS). When browsing through the resources, find the applicable standards in the lesson overview:
| Grades | 3-7 |
| Time | 1 hour |
| Resources | Video, Experiment |
| Standards | NGSS 3-5-ETS1-1 NGSS 5-PS1-3 CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.6-8.3 |
The resources you’ll find on this site are appropriate for a variety of grade levels ranging from 3rd grade to 12th grade. While each lesson will suggest the grade range it is appropriate for, we encourage instructors to adapt lessons for their student’s specific skill levels.
The FarmBot Inc developed open educational resources are licensed under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication. This is compliant with the definition of “open” put forth by the Open Knowledge Foundation.
In short, this means you are free to use the FarmBot Inc developed resources (text, images, tables, files, videos, etc) as you please, without attribution to FarmBot Inc or needing to request permission. This includes viewing, copying, modifying, and redistributing the content for any purpose, even commercial purposes. This content comes with no warranty, express or implied.
Some resources on this site were not developed by FarmBot Inc and thus may not be licensed the same. For example: embedded YouTube videos that are not from the FarmBot Inc YouTube channel.
Please read and respect the individual licenses of any 3rd party content.
https://genesis.farm.bot/v1.7/extras/troubleshooting
https://genesis.farm.bot/v1.7/extras/maintenance
The powerful web app, custom operating system, and firmware that bring FarmBot to life
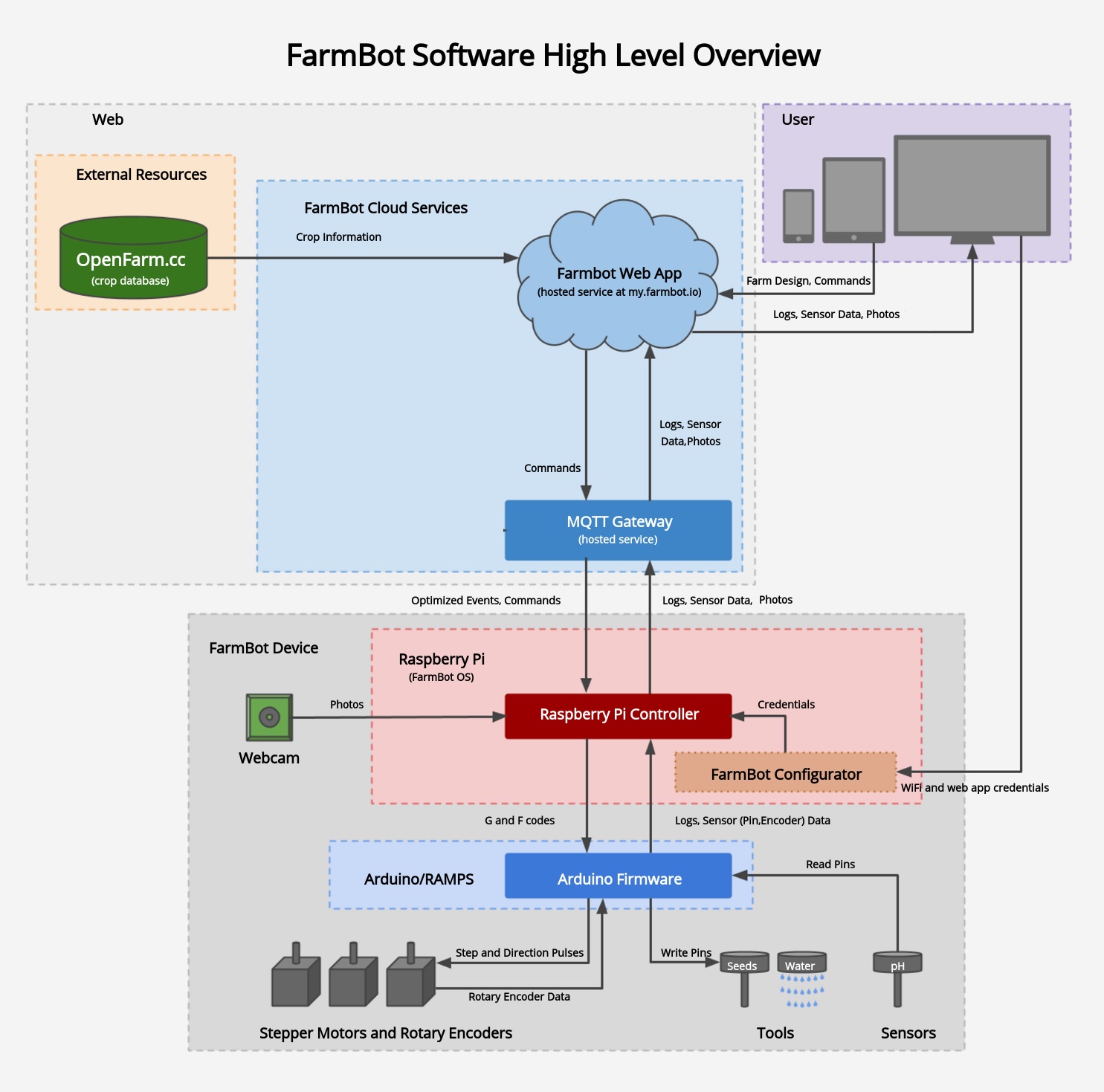
There are many software systems contributing to FarmBot’s functionality. The diagram below shows the different components and how data flows between them. Read the brief descriptions of each component in the following sections to understand the system as a whole, and then dive into setting up the needed components for your FarmBot.
All of our software is licensed permissively, allowing you to contribute to, copy, modify, redistribute, and even sell FarmBot software. Want to help build new features or have a bug to report? Get involved on GitHub!.
Have a question or need help setting up some of the software?
The Raspberry Pi is the communications link to the FarmBot Web App. The Raspberry Pi communicates directly with the Farmduino board. The Farmduino is the central component of the FarmBot from a electronic systems perspective. This diagram shows how all of the FarmBot components interact with the Farmduino with the Raspberry Pi acting as the communications node between the Web App and the Farmduino.
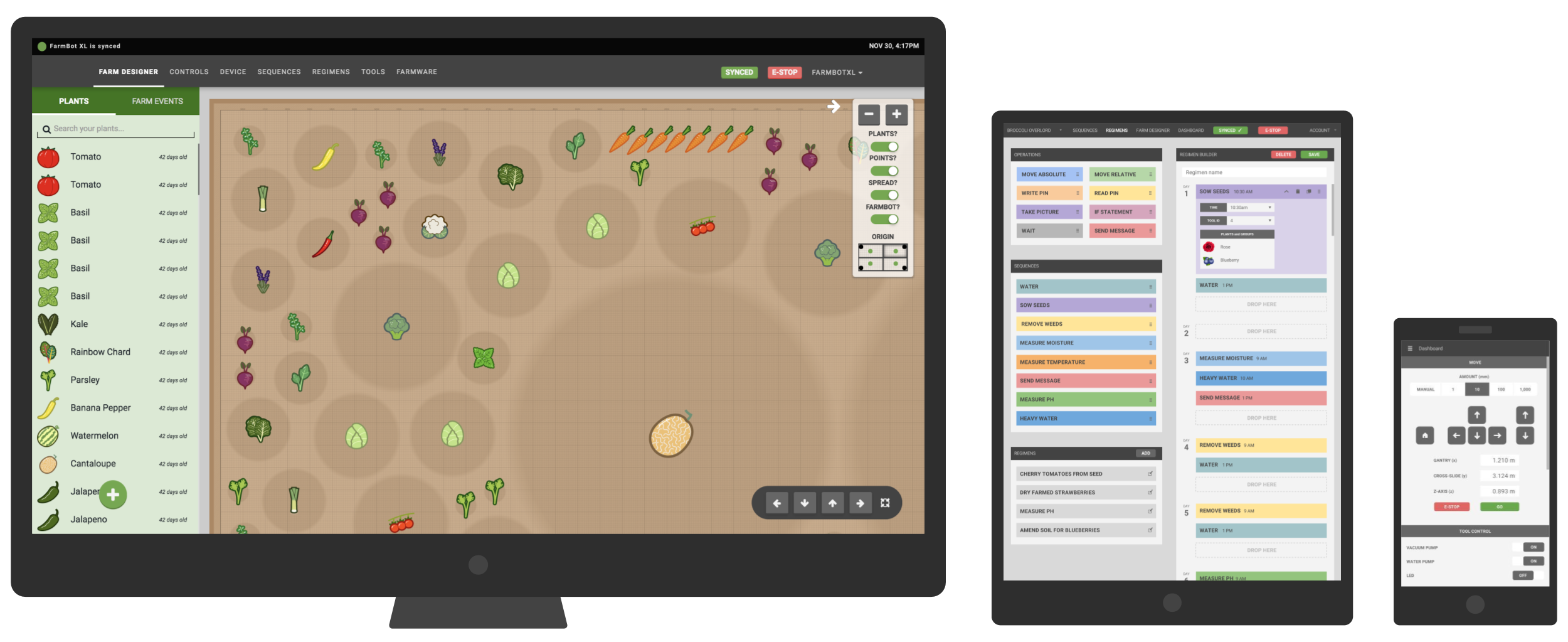
The web app allows you to easily control and configure your FarmBot from a web browser using your laptop, tablet, or smartphone. The application features real-time manual controls and logging, a sequence builder for creating custom routines for FarmBot to execute, and a drag-and-drop farm designer so you can graphically design your garden.
FarmBot’s Raspberry Pi runs a custom operating system named FarmBot OS to maintain a connection and synchronize with the web application via the message broker. This allows FarmBot to download and execute scheduled events, be controlled in real-time, and upload logs and sensor data. The OS communicates with the Farmduino/Arduino over a USB cable or serial connection to send G and F code commands, and also receive collected data from sensors and rotary encoders.
FarmBot OS has a built-in utility named configurator allowing you to easily enter WiFi and web app credentials from a WiFi enabled device (such as a laptop or smartphone). This is used for initial setup in order to get your FarmBot connected to your home WiFi and web app account.
The firmware that is flashed onto the Arduino or Farmduino microcontroller is responsible for physically operating FarmBot’s motors, tools, sensors, and other electronics. It receives G and F codes from FarmBot OS, and then moves the motors and reads and writes pins accordingly. It also sends collected data from the rotary encoders and pin reads back to the Raspberry Pi.
OpenFarm is a free and open database for farming and gardening knowledge. This service provides crop and growing information to the web app for a streamlined user experienced.
OpenFarm was originally conceived as a small component of the FarmBot project. As progress was made, it became clear that OpenFarm had no reason to be tied to FarmBot, but could rather live on its own. In September of 2014, 1,605 people backed OpenFarm on Kickstarter. Today, OpenFarm is a standalone application, non-profit, and community. You can get involved with OpenFarm by joining the Slack channel, contributing on GitHub, or going to OpenFarm and creating content!